SIRC概述 & 会员
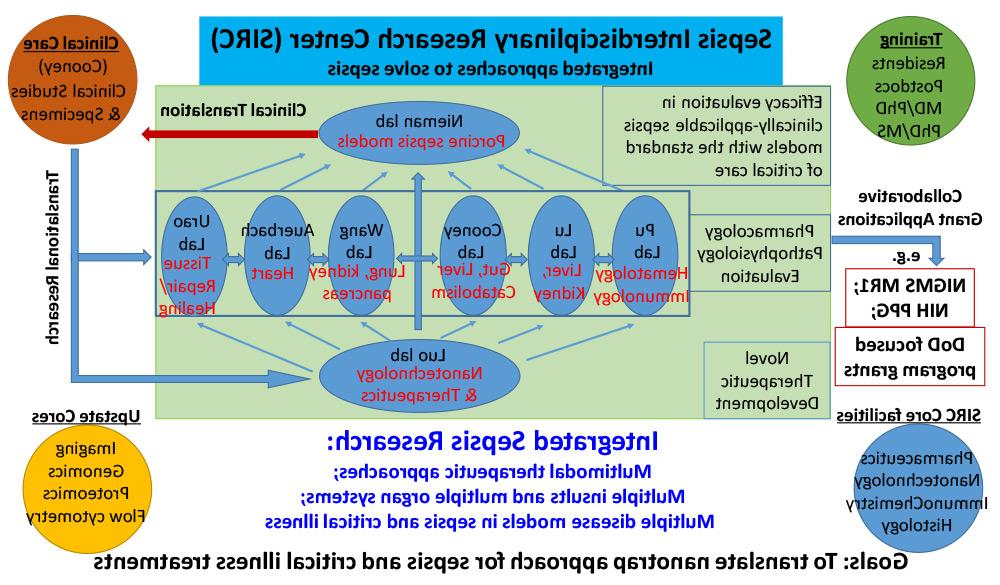
A full spectrum of interdisciplinary research expertise and multiple funded research programs (four NIH R01s) have emerged concurrently at 推荐最近最火的赌博软件, 具有进行协作和转化败血症研究的天然协同作用. The establishment of SIRC will strongly stimulate such collaborations with the goal to translate the novel technologies and therapeutics into better sepsis treatment. 外科科室有八个研究实验室, Pharmacology and Medicine have been working together closely with multiple collaborative and translational research projects related to inflammation and organ damage in sepsis and critical illness.

罗伯特·库尼, MD, 外科教授兼系主任, is a general surgeon with board certification in Surgical Critical Care who has cared for critically ill patients with sepsis and organ failure for over 28 years. 除了 to serving as the PI on multiple clinical trials for sepsis and organ failure, he is also a NIH funded investigator with over two decades of laboratory-based research on sepsis-induced catabolism, 肠道和器官损伤. Dr. 库尼组织了一个多学科的, translational research group in the Department of Surgery with overlapping research interests in sepsis and organ injury.

Juntao罗, 博士学位, 药学系、外科学系副教授(联合), focuses on the development of novel therapeutic approaches and nanotechnologies for disease treatments. Dr. 罗发明了一部小说, well-defined telodendrimer nanoplatform for customized nanocarrier development for the delivery of various therapeutics, 包括小分子, 蛋白质治疗和基因分子. 此外,博士. 罗将他的药物传递纳米平台转化为纳米颗粒中的分子陷阱, nanogel, 水凝胶和水凝胶树脂, 哪些可以用来运送治疗药物, 以及清除损伤分子和炎症介质, 因此, 减轻败血症的过度炎症. Dr. Luo has been actively collaborating with many SIRC faculty to apply his nanotechnologies to improve treatment of critical illness associated with sepsis.

Guirong王, 博士学位, 外科教授, studies the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which the surfactant proteins -A (SP-A) and –D (SP-D) modulate the host response to infection. Dr. Wang’s NIH- and NSF-funded laboratory uses genetically modified SP-A and SP-D knockout and humanized transgenic mouse models to elucidate their role in pneumonia-induced sepsis and organ dysfunction. 此外,博士. 在过去的十年里,王一直与SIRC的其他小组密切合作.

加里·尼曼, BA, 外科教授, has developed a highly clinically-applicable porcine sepsis model induced by both traumatic injury and infections. His lab has applied this powerful sepsis model for two decades in evaluating therapeutic modalities to prevent lung injury and other organ failures. He and his group have developed an innovative protective mechanical ventilation strategy to reduce the incidence and mortality of sepsis-induced ALI, 目前在上州医院的重症监护室使用的药物. 多项联邦拨款已被授予.g. R01, R21,国防部拨款,SBIR奖等. using this clinically-relevant large animal model that very closely simulates all of the components in a clinical ICU. Professor Nieman currently is the PI on a NIH grant to study protective mechanical ventilation in ALI collaborating with the University of Vermont and Tulane. 除了, Professor Nieman is a coinvestigator on an R01 with the University of Rochester and with Dr. 罗在上州.

香港路, 博士学位, 药学系助理教授, 从事肝脏疾病和肝功能研究20多年了吗. 他一直在与博士合作. 罗在开发肝脏特异性皮质类固醇前药, 由美国国立卫生研究院资助, to protect hepatocyte function and improve anti-inflammatory response to treat alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cirrhosis, 脓毒症的主要危险因素. 他也一直在与博士合作. Luo to study how liver-specific deficiency and activation of glucocorticoid receptor affect sepsis outcomes.

大卫•奥尔巴赫, 博士学位, 药学系助理教授, 努力推进对神经心脏电障碍的理解. 他的心律失常研究项目目前由美国心脏协会资助. Dr. 奥尔巴赫的研究项目是对本项目目标的补充, 他领导着一个多系统、多学科的研究项目. 他在神经心脏细胞,器官, 在活的有机体内, 以及临床数据库研究方法, which will enable detailed investigations into the implications that sepsis has on cardiac function.

Norifumi Urao, MD /博士, 药学系助理教授, 获得NIH/R01组织修复/愈合资助, 骨髓反应和先天免疫. 作为一名具有内科和心脏病学临床经验的研究科学家. 我们的重点是获得缺血性器官损伤的知识. His research interests include wound healing/tissue regeneration after ischemic damage and the long-term impacts of obesity/diabetes on the immune system.

Michaela (Mikki) kolisch, MD, 儿科外科助理教授, 和加里·尼曼教授一起研究败血症和肺损伤. 有数学背景, 她一直在研究脓毒症引起的肺损伤动物模型的肺微观力学. She determined that subtle changes in mechanical ventilation parameters lead to marked changes in alveolar and alveolar duct recruitment, 形状, 和分布. Understanding these micromechanical changes is crucial to developing protective mechanical ventilation strategies that minimize ventilator induced lung injury and the resultant acute respiratory distress syndrome.

Snehalata帕瓦尔, 博士学位, 放射肿瘤学助理教授, studies sepsis in the context of ionizing radiation (IR)-induced damage to radiation to normal tissues (intestine).
A major side-effect of exposure to whole body radiation such as explosion of a nuclear bomb or during a nuclear accident or during abdominal radiotherapy is the acute toxicity of IR to the rapidly renewing cell systems such as the bone marrow (BM) and gastrointestinal (GI) tract mucosa. 目前, 目前还没有有效的药物来预防或治疗红外诱发的肠道败血症, and 因此 delineating the cellular and molecular mechanisms of sepsis is of utmost importance in developing future therapies.
She has been studying the molecular mechanisms of radiation-induced intestinal injury and sepsis and identified TLR4 signaling as a potential target for intervention to protect against intestinal inflammation and nitrosative stress. Dr. Pawar’s current studies examine the role of TLR4 inhibition in protection from a) acute radiation-induced damage to intestinal stem cells and b) from delayed radiation-induced damage to the heart. Another ongoing project is to investigate the role of a small molecule drug- Myelo001 in protection against radiation-induced damage to hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.