散点去除网格
的 antiscatter grid plays an important role for enhancing image quality in projection radiography by transmitting a majority of primary radiation and selectively rejecting scattered radiation. This device is comprised of a series of thin lead strips separated by radiolucent interspaces in a form-factor that matches the detector size. Most grids have a linear geometry in one direction (usually along the long axis of the detector). 平行栅格有聚焦到无限远的引线条.e. 初级x射线有平行的轨迹。. Focused grids have lead strips that are oriented parallel at the center (along the x-ray central axis) and progressively slanted to the periphery to match the beam divergence from the focal spot .到探测器处的特定源到探测器的距离.
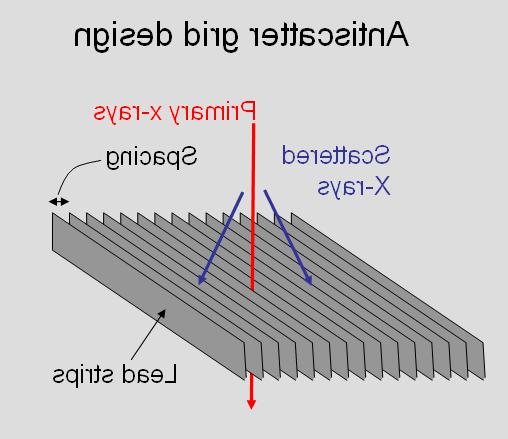
的 anti-scatter grid is typically manufactured with lead strips oriented along one dimension separated by a low attenuating interspace material such as carbon fiber or aluminum. 用于特殊应用, 在两个方向上都有交叉的网格(铅条), perpendicular to each other) for specialized applications such as dedicated chest imaging, and in mammography where a "cellular" grid design made of copper with air interspaces is used clinically by one manufacturer. By selectively allowing primary x-rays to be transmitted and scattered x-rays to be absorbed in the grid, image contrast is significantly enhanced; 然而, the grid attenuates some of the desired primary x-rays that are incident directly on the lead strips and allows transmission of some scattered radiation photons that have a small scattering angle, 或者沿平行于铅条的方向分散, or are multiply scattered with an exit angle from the patient that can be transmitted through the grid.
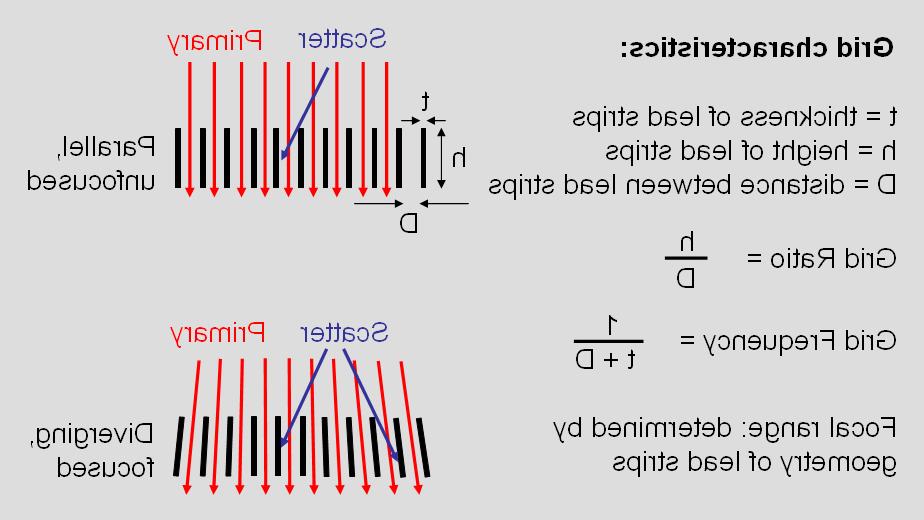
Grids are chiefly characterized by the 网格比, 电网频率, and 焦距. 的 网格比 引线带的高度是空间距离的度量吗, 是衡量主向散射传输选择性的一个很好的指标. 在一般情况下, a grid with a higher 网格比 will reject scatter better than a lower 网格比, 由于网格结构允许的角度有限. 然而, a higher ratio grid typically has a higher dose penalty for its use (for screen-film imaging this is known as the "Bucky Factor" which represents the increased dose to the patient when using a grid compared to not using a grid when the film optical density is matched). 使用数码成像, 当使用网格时,也有剂量惩罚, and the benchmark is the signal to noise ratio (as opposed to film optical density). 的 电网频率 is a measure of the number of grid lines per unit distance (inches or centimeters), and is in the range of 40 - 50 lines/cm (100-120 lines/inch) for low frequency grids, 50-60线/厘米(120 - 150线/英寸)中频网格, 60 - 70+线/厘米(150-170+线/英寸). Low frequency grids are used with systems having a moving grid assembly (known as a Bucky device) that oscillates during the exposure to blur the grid lines. 中频和高频栅格通常与固定栅格支架一起使用.g.便携式放射照相和许多数字放射照相系统). High frequency grid use is particularly important for digital radiography systems to avoid aliasing artifacts (see section on radiography artifacts) that arise from insufficient sampling of high frequency patterns that are interpreted in the output signal as low frequency (aliased) signals. 网格 焦距 is determined by the angle of the lead strip geometry that is progressively increased from the center of the grid to the periphery, 为了解释从焦点点发出的发散的主x射线束. 典型的焦距是100厘米(40英寸)和180厘米(72英寸)。, 虽然有许多专门的网格焦距. 焦范围 is an indicator of the flexibility of grid positioning distance from the focal spot, 是网格比和频率的函数. 便携式放射照相的通用栅格具有相当大的范围(例如.g.(80至130厘米),而特殊用途网格的焦距要窄得多. 网格伪影产生于网格设备的不正确定位, such as tilting the grid at a non-perpendicular direction to the incident x-ray beam, 网格没有对准x射线束的中轴线, 使用指定焦距范围之外的聚焦网格, and placing the grid upside down (converging geometry is directed opposite of the focal spot).
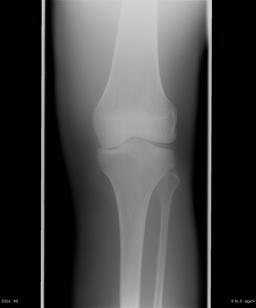

的 two images of the AP projection of the knee phantom were obtained at 60 kV at the table top (left) and using the scatter removal grid (Bucky) (right). 两幅图像的最终S数均为~350, indicating an air kerma incident on the computed radiography imaging plate of ~6 uGy (0.6). 左边的桌面图像, 然而, 需要3毫安的技术,而右边的需要10毫安, since the scatter removal grid removes most of the scattered photons that emerge from the phantom. 因此巴基因子是3.3 (i.e., 10 ma /3 ma), and this is a quantitative measure of the increase in patient dose resulting from the use of the scatter removal grid. Note the improvement in image quality achieved by removal of most of the scatter radiation.
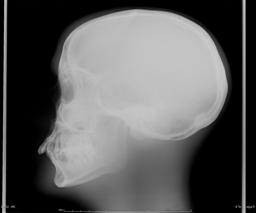
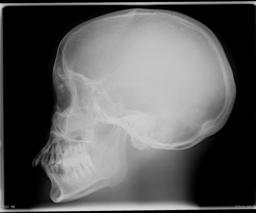
的 two lateral projection images of the skull phantom were obtained at 75 kV at the table top (left) and using the scatter removal grid (i.e.(巴基)(右). 两幅图像的最终S数均为~100, indicating an air kerma incident on the computed radiography imaging plate of ~20 uGy (2 mR) in both cases. 左边的桌面图像, 然而, 需要4毫安的技术,而右边的需要20毫安的技术, since the scatter removal grid removes most of the scattered photons that emerge from the phantom. 因此,巴基因子是5 (i).e., 20 ma /4 ma), and this is a quantitative measure of the increase in patient dose resulting from the use of the scatter removal grid. Note that there is a dramatic increase of image quality achieved by removal of most of the scatter radiation, 对病人来说,额外的辐射剂量是值得的.


的 two AP projection images of the pelvis phantom were obtained at 75 kV at the table top (left) and using the scatter removal grid (Bucky) (right). 两幅图像的最终S数均为~240, indicating an air kerma incident on the computed radiography imaging plate of ~8 uGy (0.两种情况下均为8mr). 左边的桌面图像, 然而, 需要3毫安的技术,而右边的需要25毫安, since the scatter removal grid removes most of the scattered photons that emerge from the phantom. 因此,巴基因子是8 (i).e., 25ma / 3ma), and this is a quantitative measure of the increase in patient dose resulting from the use of the scatter removal grid. Note that there is a dramatic increase of image quality achieved by removal of most of the scatter radiation, 对病人来说,额外的辐射剂量是值得的.
Also note that the Bucky factor for the abdomen is substantially higher than those for the knee and the skull radiographs; 的 reason for this is that scatter is reduced with decreasing kV, as well as when imaging predominantly bony structures where most interactions are through the photoelectric effect (Compton scatter dominates for radiographs of soft tissue structures).